We have designed and manufactured over 1500 industrial furnaces, catering to various industries such as automotive, steel, and chemical. With extensive experience and a proven track record in a wide range of furnace types, we offer a diverse range of solutions. In addition to industrial furnaces, we provide total support for related equipment and conveyors, and have successfully tackled a multitude of challenges based on different specifications and needs.
Explanation of atmosphere gas for heat treatment: types, applications, and generation equipment.
In recent years, there has been a growing demand for improvements in safety, cost-effectiveness, and environmental impact in the manufacturing of automotive parts and other similar industries that heavily rely on heat treatment equipment. As a result, sealed-type furnaces have become more prevalent, and the atmosphere gas used inside the furnace has been drawing attention.
The type of atmosphere gas used in the furnace can significantly impact the quality and cost of the product depending on its purpose and application. Therefore, it is crucial to carefully select the appropriate gas for the desired outcome.
In this article, we will explain the background and uses of atmosphere gas, as well as its various types. Additionally, we will provide a detailed explanation of the equipment used to generate atmosphere gas.
目次
What is atmosphere gas?
Atmosphere gas refers to the gas used by filling it in a heat treatment furnace.
Let’s first discuss some basic information about atmosphere gas.
Applications of atmosphere gas in heat treatment
In heat treatment, when materials are treated in the air, they tend to oxidize or decarburize, resulting in a thick oxide scale formation on the surface. This requires peeling treatment in subsequent processes, which can be time-consuming and wasteful.
However, using atmosphere gas can eliminate or suppress the oxidation reaction of the treatment material, thereby reducing the effort required for peeling treatment and eliminating material waste.
Atmosphere gas is not only used to prevent oxidation but also for other purposes.
- Preventing oxidation:By preventing the formation of oxidation films caused by the reaction with oxygen
- Preventing decarburization:By preventing the loss of carbon from steel, which can result in strength reduction
- Carburizing treatment:By penetrating carbon into the surface of steel to improve its strength
- Nitriding treatment:By penetrating nitrogen into the metal surface to improve its characteristics
Atmosphere gases used in heat treatment
Various gases with different properties are used as atmosphere gases in heat treatment.
The main types and classifications of gases are as follows:
| Types: | Classification: |
|---|---|
| Inert gases | Nitrogen, argon, helium, etc. |
| Oxidizing gases | Oxygen, water vapor, etc. |
| Reducing gases | Hydrogen, ammonia, decomposition gas, etc. |
| Carburizing gases | Carbon monoxide, hydrocarbon gas, city gas, propane gas, methanol, etc. |
In heat treatment, it is sometimes more cost-effective to use gases that are generated by mixing these gases with air or subjecting them to chemical reactions or electrolysis, rather than using pure gases.
Classification and types of atmosphere gas used in heat treatment
Next, we introduce the types of atmosphere gas produced using various gases as raw materials, which we mentioned earlier, called atmosphere gas generated by transformation.
We explain four representative types of atmosphere gas classified by differences in the method of generation.
Exothermic atmosphere gas (DX gas, NX gas)
DX gas and NX gas are produced using gases such as propane gas and butane gas.
The DX gas is obtained by combusting these gases and removing water and adjusting the composition.
The exothermic atmosphere gas is classified into lean and rich types depending on the amount of air mixed.
Additionally, nitrogen atmosphere gas (NX gas) is obtained by removing carbon dioxide and water from the combustion gas.
Endothermic atmosphere gas (RX gas)
In contrast to exothermic atmosphere gas, endothermic atmosphere gas does not generate heat on its own and requires external heat supply for reaction.
Therefore, it is called endothermic atmosphere gas.
By heating hydrocarbon gases such as propane to over 1000℃ and keeping them with nickel as a catalyst, endothermic atmosphere gas (RX gas) is generated.
Ammonia decomposition gas (AX gas)
Ammonia decomposition gas (AX gas) is generated by decomposing vaporized ammonia gas into hydrogen and nitrogen through a nickel catalyst at approximately 1000℃.
Ammonia decomposition gas is also attracting attention for purposes other than heat treatment because hydrogen is generated.
Drip-type decomposition gas
This gas is generated by directly dropping organic solvents such as methyl alcohol into a high-temperature furnace to thermally decompose them.
Compared to transformation gas, the CO gas concentration is higher, and carbon infiltration treatment can be performed more quickly than with conventional transformation gas.
| Type | Common name | Composition (%) | Dew point | Applications | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO | CO2 | H2 | CH4 | N2 | ||||
| Exothermic gas | Lean DX gas | 1.5 | 12.5 | 0.8 | – | Residual | +5 | Non-oxidizing annealing |
| Rich DX gas | 12.0 | 6.5 | 10.0 | 0.5 | Residual | +5 | Bright annealing Brazing |
|
| Nitrogen-based gas | Nitrogen DX gas | 1.8 | 0.05 | 1.0 | – | Residual | -40 | Bright annealing Non-oxidizing quench hardening Sintering |
| Endothermic gas | Endothermic RX gas | 24.0 | 0.3 | 33.4 | 0.4 | Residual | 0 | Carburizing Carburizing and nitriding Bright annealing Bright quench hardening Sintering Brazing |
| Ammonia decomposition gas | Ammonia decomposition AX gas | – | – | 75.0 | – | Residual | -40 | Reduction Bright annealing Bright quench hardening Sintering Brazing |
| Dripping decomposition gas | – | 20.0 | – | 80.0 | – | – | – | Carburizing |
Transforming atmosphere gas generation equipment
In our previous article, we explained the types and uses of atmosphere gas. Now, we will delve into the topic of atmosphere gas generators. Specifically, we will discuss the benefits of transformation atmosphere gas generators and their structure.
Advantages of transforming atmosphere gas generation equipment
Let us first explain the benefits of atmosphere gas generators.
Cost reduction
By introducing atmosphere gas generators, it is possible to produce expensive hydrogen or nitrogen gas internally, thereby reducing manufacturing costs.
Reuse of exhaust gas
Moreover, by reusing the heat generated by the generator according to the intended purpose, it is possible to reduce the amount of electricity and city gas used in factories. Conversely, it is also possible to generate atmosphere gas by using the exhaust gas generated by gas combustion.
Adjustment of gas concentration
Generating atmosphere gas internally makes it possible to adjust the gas concentration, making it easy to set the appropriate gas concentration for one’s own products.
Structure of transforming atmosphere gas generation equipment
Let us use the example of the endothermic reaction gas (RX gas) generator to explain the structure of atmosphere gas generators.
An endothermic gas generator is mainly composed of the following elements:
- Transformation furnace
- Reaction tower (catalyst)
- Burner
- Cooler
- Piping
First, the raw gas and air are mixed in a mixer and sent to the reaction tower.
The catalyst inside the reaction tower is heated to around 900℃ by the burner, and the reaction of the mixed gas progresses.
Nickel is mainly used as the catalyst.
The generated endothermic gas passes through the cooler, is cooled, and is then sent out.
The diagram below shows the overview of the structure.

Types of transforming atmosphere gas generation equipment
In this article, we will introduce several types of atmosphere gas generators that have been implemented in the past at Sun Furnace.
Ammonia decomposition gas generator (AX Gas)
By devising a dehydration treatment method that continuously emits a small amount of gas when ammonia is passed through, it became possible to perform heat treatment without stopping the equipment.
[Challenge before implementation]
Process stopped due to moisture generated during heat treatment
[Effect after implementation]
By incorporating two water adsorption towers and exchanging them around the clock, it became possible to operate the equipment without the need to stop it or replace spares.

Heat-generating transforming gas generator (DX Gas)
By changing the cooling method of the generated gas, the cycle could be shortened, and efficient heat treatment became possible.
[Challenge before implementation]
Wanted to quickly cool and use the generated gas
[Effect after implementation]
By using a special two-stage cooling method, gas could be cooled faster than with conventional water cooling, enabling heat treatment without time loss.
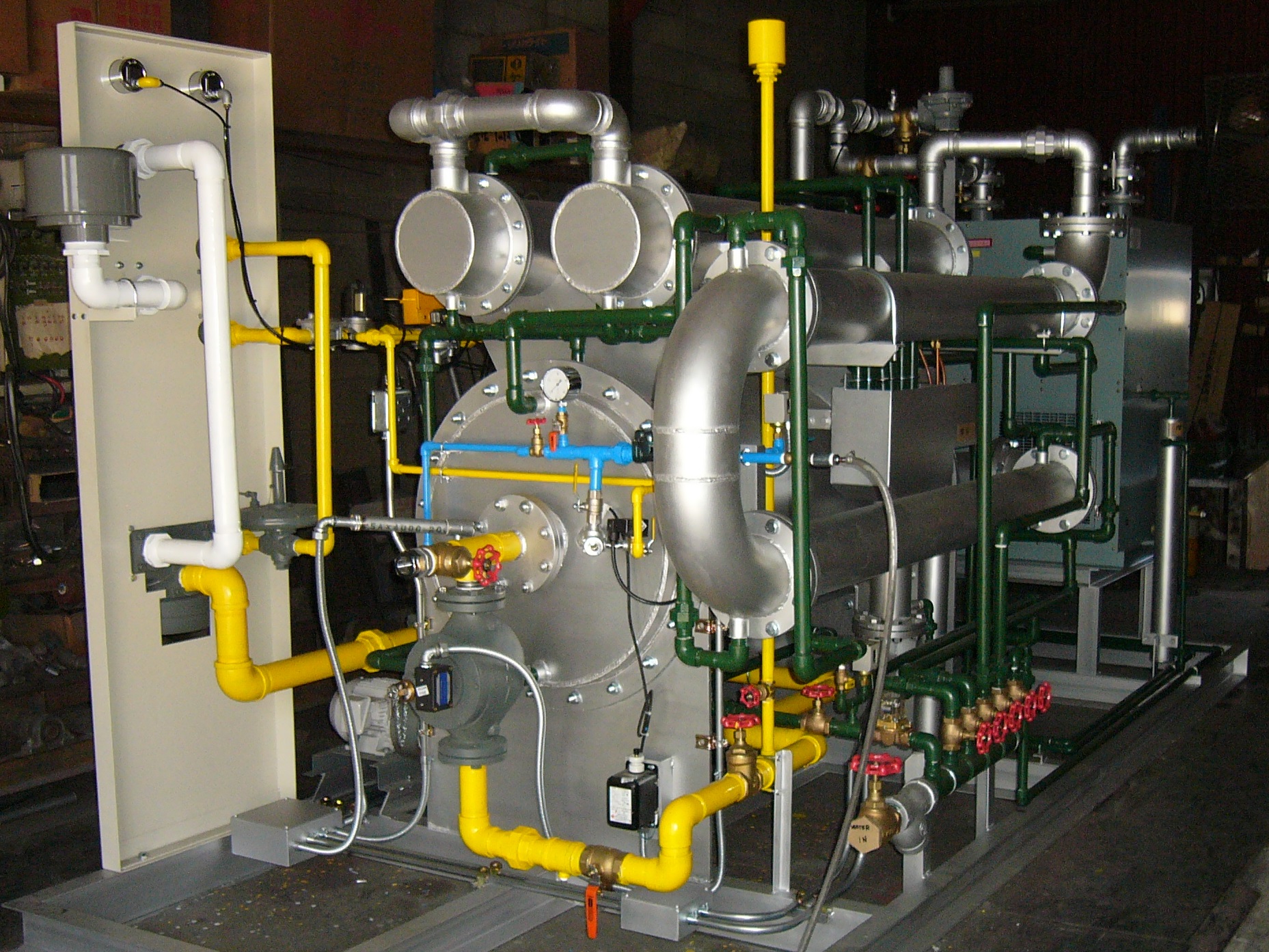

Heat-absorbing transforming gas generator (RX Gas)
By improving the muffler, it became possible to prevent muffler embrittlement caused by metal dusting phenomena.
[Challenge before implementation]
Muffler cracks due to the atmosphere inside the muffler and the processing temperature of the RX gas
[Effect after implementation]
By changing the material of the muffler, adjusting its thickness, and devising a connection method with the piping, the muffler’s lifespan was extended.

Frequently asked questions
Q: What is the difference between using the inert gases argon and nitrogen?
Nitrogen and argon are both used as inert gases, but nitrogen has the characteristic of reacting with certain metals at high temperatures.
Argon is a more stable substance, but it can cost around twice as much as nitrogen gas.
Therefore, it may be advisable to use them according to their intended application.
Q: Are there any risks of fire or explosion from using transforming atmosphere gas?
Modified atmosphere gases may contain highly flammable gases, and if they accidentally mix with air and reach explosive concentration, they can explode due to electric sparks, among other reasons.
Since removing ignition sources in heat treatment equipment is impossible, attention must be paid to safety design to prevent air mixing.
Propane gas and methane gas have relatively narrow explosion limits, but they can cause fires if leaked carelessly.
It is essential to be very careful about fire prevention, such as installing detectors and ventilating the area.
Q: What are the advantages of using modified atmosphere gas for brazing in a furnace?
Inert gases like nitrogen and the reducing gas hydrogen are frequently employed in furnaces for brazing.
By reducing the iron oxide back to iron with the aid of a reducing gas, the glossy appearance can be recovered.
Utilizing nitrogen can also keep a substance from oxidizing and stop oxidation.
Summary
So far, we have explained the types and characteristics of atmosphere gases and manufacturing equipment.
Hydrogen and nitrogen are commonly used as atmosphere gases in heat treatment furnaces, and are used to prevent oxidation and promote carburization.
By selecting the appropriate atmosphere gas for use, it is possible to improve product performance and reduce costs.
Industrial furnace manufacturer, Sun Furnace, proposes custom-made atmosphere gas generation devices tailored to your application based on the know-how gained from manufacturing more than 1,500 industrial furnaces. We also offer free technical consultations, so please feel free to contact us.



