We have designed and manufactured over 1500 industrial furnaces, catering to various industries such as automotive, steel, and chemical. With extensive experience and a proven track record in a wide range of furnace types, we offer a diverse range of solutions. In addition to industrial furnaces, we provide total support for related equipment and conveyors, and have successfully tackled a multitude of challenges based on different specifications and needs.
In this article, we will explain what bright annealing is and how it differs from atmospheric annealing, as well as its various applications.

For engineers who are looking to achieve a glossy surface finish on materials used for new products, understanding the process of bright annealing can be essential.
This includes the types of structures and systems available for bright annealing furnaces, as well as the basic principles behind its operation. In this article, we will explore the basic mechanisms and advantages of bright annealing, and provide useful information for those interested in installing a bright annealing furnace.
Unlike traditional annealing processes, which can produce a blackened metal surface due to oxidation, bright annealing can be used to achieve a beautiful glossy finish on metal surfaces without darkening.
This process involves heating the metal to a high temperature to improve its overall properties while imparting a bright, lustrous finish.
However, it is important to be mindful of the process conditions, such as atmospheric gases and temperature, as these can greatly impact the final result.
To ensure success with bright annealing, it is essential to have a thorough understanding of the furnace structure and operating conditions.
This article will provide comprehensive information on the mechanisms and benefits of bright annealing, as well as the types of structures and systems available for bright annealing furnaces. If you are looking to achieve a high-quality, glossy finish for your materials, then the information provided in this article will be invaluable.
目次
What is bright annealing?
Difference between atmosphere annealing
Annealing is a heat treatment process used to remove residual stresses and work hardening from metal materials.
Annealing can make the crystal structure of the metal material uniform and soft, which can improve the workability and toughness of the metal.
Atmosphere annealing is a method of annealing where atmospheric gases are used during the heating process. When metal is heated in the presence of atmospheric gases, the metal surface reacts with oxygen to form an oxide film.
Removing this oxide film requires additional steps such as polishing or acid washing, which can be time-consuming. In order to avoid using atmospheric gases, inert gases such as nitrogen or argon can be used for annealing, which is called “non-oxidizing annealing.”Since no oxide film is generated on the metal surface, the metal’s luster can be maintained. Also, since no carbon is used, there is no change in the hardness of the metal due to carburization.
One type of non-oxidizing annealing is bright annealing, which uses reducing gases such as hydrogen to prevent the product from becoming discolored during heat treatment. Managing the atmosphere inside the furnace, including oxygen concentration and dew point, is important for bright annealing.
Atmosphere gas for bright annealing
In bright annealing, the furnace is filled with atmosphere gas during heat treatment. In addition to preventing oxidation and decarburization, an appropriate atmosphere gas is selected for the desired outcome.
Cost is also a consideration when choosing an atmosphere gas.
Currently, it is more common to use low-cost gases such as nitrogen or ammonia decomposition gas, rather than inert gases such as argon that can lead to cost increases.
The type of atmosphere gas generated by the atmosphere gas generator called the atmosphere furnace varies depending on the type of furnace and is referred to as exothermic atmosphere gas, endothermic atmosphere gas, or ammonia decomposition gas.
The types of atmosphere gases mainly used and their general applications are as follows.
| Types of gases | Common name | Main use |
|---|---|---|
| Heat-generating type conversion gas (rich) | DX(R) | Low carbon steel |
| Heat-generating type conversion gas (dry) | DX(DRY) | Aluminum |
| Nitrogen-based conversion gas | NX | Steel and aluminum |
| Heat-absorbing type conversion gas | RX | Medium to high carbon steel |
| Ammonia decomposition gas | AX | Stainless steel |
| Hydrogen-nitrogen mixed gas | HN | Steel sheet coils ・ yellow steel coils |
| Argon gas | – | Ti and Zr alloys |
Temperature conditions for bright annealing
Depending on the material and shape of the item being treated, specific temperature conditions must be selected to ensure optimal results.
We will introduce past cases of San Furnace’s implementation based on actual examples.
Temperature conditions for bright annealing of wire products
| Processing materials | Wire diameter (mm) | Heating capacity (kW) | Temperature (℃) |
|---|---|---|---|
| High carbon steel wire | φ0.03~φ0.2 | 9 | 700 |
| Pipes of beryllium copper, stainless steel, titanium, brass, etc. | φ1.0~φ6.0 | 12 | 400~1,150 |
| Copper alloys, stainless steel | φ0.1~φ0.32 | 18 | ~1,000 |
| Steel wire | φ0.45~φ0.63 | 30 | 1,000 |
| Stainless steel wire | φ0.2~φ1.0 | 48 | 1,175 |
| Titanium wire | φ0.2~φ6.0 | 60 | 700~800 |
| Special steel wire | φ1.0 | 60 | 300~1,100 |
| Steel wire such as SUS304 and SUS316 | φ1.0 | 78 | 1,120 |
| Solution treatment of stainless steel wire | φ2.0~φ5.5 | 160 | 1,120 |
Temperature conditions for bright annealing of plate materials
| Processing materials | Plate width (mm) | Plate thickness (mm) | Heating furnace length (mm) | Heating capacity (kW) | Temperature (℃) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SUS304, SUS430, Ti alloy | 450 | 0.015~0.2 | 9,100 | 337 | 1,100 |
| SUS304, SUS430, Ti alloy | 530 | 0.005~0.2 | 7,000 | 378 | 1,100 |
| SUS304, copper, 42Ni | 650 | 0.1~1.0 | 8,900 | 500 | 750 |
| SUS301, SUS304, Mg alloy | 700 | 0.03~0.2 | 9,800 | 417 | 1,100 |
| SUS301, SUS430 | 800 | 0.3~1.5 | 17,000 | 1,350 | 1,150 |
| Copper, brass, 42Ni | 200 | 0.1~1.0 | 5,500 | 75 | 600 |
| Copper, brass | 420 | 0.1~1.0 | 13,500 | 300 | 750 |
Applications of bright annealing
Advantages of bright annealing
Bright annealing is a type of annealing that falls under the category of non-oxidizing annealing.
It involves heat treatment in an oxygen-free environment, which prevents the material’s surface from being exposed to oxygen and the formation of an oxide film.
This process is commonly used when preserving the material’s surface finish is important, as it maintains the surface’s shine.
In addition to this, bright annealing has excellent compatibility with special steels, making it a popular choice in the industry.
Objectives of bright annealing
Electrolytic bright annealing is performed for a variety of purposes, including preventing oxidation of the metal surface.
- Providing a lustrous finish to metal surfaces
- Lowering the hardness of stainless steel
- Eliminating residual stress and work hardening in stainless steel
- Brazing of metal substrates
Examples of applications of bright annealing
Bright annealing has a wide range of applications across various industrial fields.
Some of the most common applications
| Examples of use | Utilized components or utilization purposes |
|---|---|
| Annealing of austenitic stainless steel | Straight pipes, flexible tubes, and round rods |
| Brazing of metal substrates | Utilization in heat exchangers, electrical components, automotive parts, and gas appliances |
| Annealing of copper alloys | Processing of parts made of pure copper, brass, and phosphor bronze, among others. |
Structure and types of bright annealing furnaces
Differences in structure of bright annealing furnaces
This section explains the structure of the typical continuous furnaces used in bright annealing.
They can be broadly classified into two types based on their structural differences.
Straight type (horizontal type)
It is a furnace for heat treatment where the path from the material entry to the completed product always travels horizontally.
Since there is no inclination, this kind is appropriate for processing long materials like pipes and bars.
Any length of product can be accommodated by how the layout is set up.
Humpback type (inclined type)
The transportation path between the material inlet and the finished product output is inclined in this heat treatment furnace.
The typical design has an upward slope at the inlet and a downward slope at the outflow.
This kind is appropriate for processing press components and small parts.
Compared to the straight type, the humpback type uses less atmosphere gas and has superior stability in controlling the furnace atmosphere.
Process of bright annealing furnaces
Preheating zone
The preheating zone is installed to preheat the material in advance when the processing quantity is large, or when the material may become deteriorated or deformed due to rapid heating in the heating zone, and when rapid temperature rise cannot be achieved in the heating zone.
Heating Zone
The heating zone is composed of a furnace frame case, insulating material, heating element, and heat-resistant steel muffle. The structure is determined based on the size of the furnace and the size of the processed material.
The muffle type and muffleless type are available depending on the processing temperature and size of the processed material.
The heating element includes a metal heating element and a silicon carbide heating element, which are designed to be easily replaced from the outside to improve maintainability.
The temperature is precisely controlled using a highly accurate automatic temperature control meter to ensure a precise temperature distribution by sectional control.
This makes it possible to set the required temperature conditions for the processed material, enabling precise hardening adjustment and heat treatment with reduced deformation.
Cooling Zone
The cooling zone is generally composed of a water-cooled jacket or a blast circulation forced cooling device (jet cooler).
The cooling zone can be divided and adjusted according to the size and thickness of the processed material, allowing adjustment of the amount of water or air.
Conveying Process
For wire and thin plates, the catenary method is used to directly pull and convey the material.
For product shapes that cannot be conveyed by the catenary method, pusher type or roller hearth type using heat-resistant steel mesh belts or hoop materials are used to place the material on top.
Types of bright annealing furnaces
There are various types of bright annealing furnaces, which differ depending on the shape of the processed materials.
In this article, we will discuss two types of bright annealing furnaces: wire and plate annealing furnaces.
Wire annealing furnace (strand furnace)
A wire annealing furnace is a furnace that heats metal wire, which is wound in a coil and stretched, while passing it through an annealing tube (pipe). The size of the furnace body and annealing tube can be designed freely according to the size of the processed material.
In designing the furnace body, it is important to make it easy to exchange heaters and annealing tubes.
Another feature is the ability to control the temperature and gas supply in both the length and width directions for each annealing tube.
Check out Sun Furnace’ strand furnace for more information
Plate annealing furnace
A plate annealing furnace is a furnace that anneals thin plates of austenitic stainless steel, copper alloys, and other materials.
By making the rolls installed in the muffle vertically adjustable, the position of the rolls can be adjusted according to the thickness of the plates.
This enables the adjustment of the tension of the plates by lowering the position of the rolls for thick plates and raising the position of the rolls for thin plates, effectively utilizing the space inside the muffle.
Stainless steel processed in a plate annealing furnace is used in various applications such as gas piping for medical use, automotive parts, household appliances, kitchenware, and decorative items.
Check out Sun Furnace’ stainless steel heat treatment furnace for more information
Frequently asked questions about bright annealing
Q: What are effective methods for reducing the power consumption of a bright annealing furnace?
It may be cost-effective to maintain a low temperature rather than completely shutting down and cooling the furnace during weekends or periods of non-operation.
The temperature can be kept at a low level using the control panel’s schedule timer, which can heat the furnace before the start of the operating hours on weekdays.
Q: What are the advantages of using a bright annealing furnace for brazing?
A bright annealing furnace is used when you do not want to discolor the metal during brazing.
The furnace can also handle multiple brazing points simultaneously due to the processing taking place inside the furnace.
In addition, quenching and carburizing can be done simultaneously with brazing or after brazing.
Q: We are considering using bright annealing for a new product. Is it possible to conduct a test?
Yes, it is possible. We will first inquire about the details of the test and check if it can be handled by our equipment. Please feel free to contact us for more information.
Case studies of bright annealing furnace installation
Adaptation to multiple product types in small lots
This furnace has the capacity to manage several different small batch sizes at once. With variable wire sizes and gas atmospheres, it can heat treat a variety of materials in a single furnace.
[Pre-implementation challenges]
- Heat treatment of materials with varying diameters together.
- Heat treatment of materials with different atmospheres as required by the material.
[Post-implementation advantages]
- The furnace has multiple annealing tubes with temperature controls that facilitate simultaneous heat treatment of different diameter wires.
- Each annealing tube can switch atmosphere gas and adjust mass flow for customized heat treatment as needed.
Adaptation to Heat Treatment of Different Plate Thicknesses
It is possible to adjust the settings according to the thickness of the material, which enables it to handle a variety of thicknesses in one furnace.
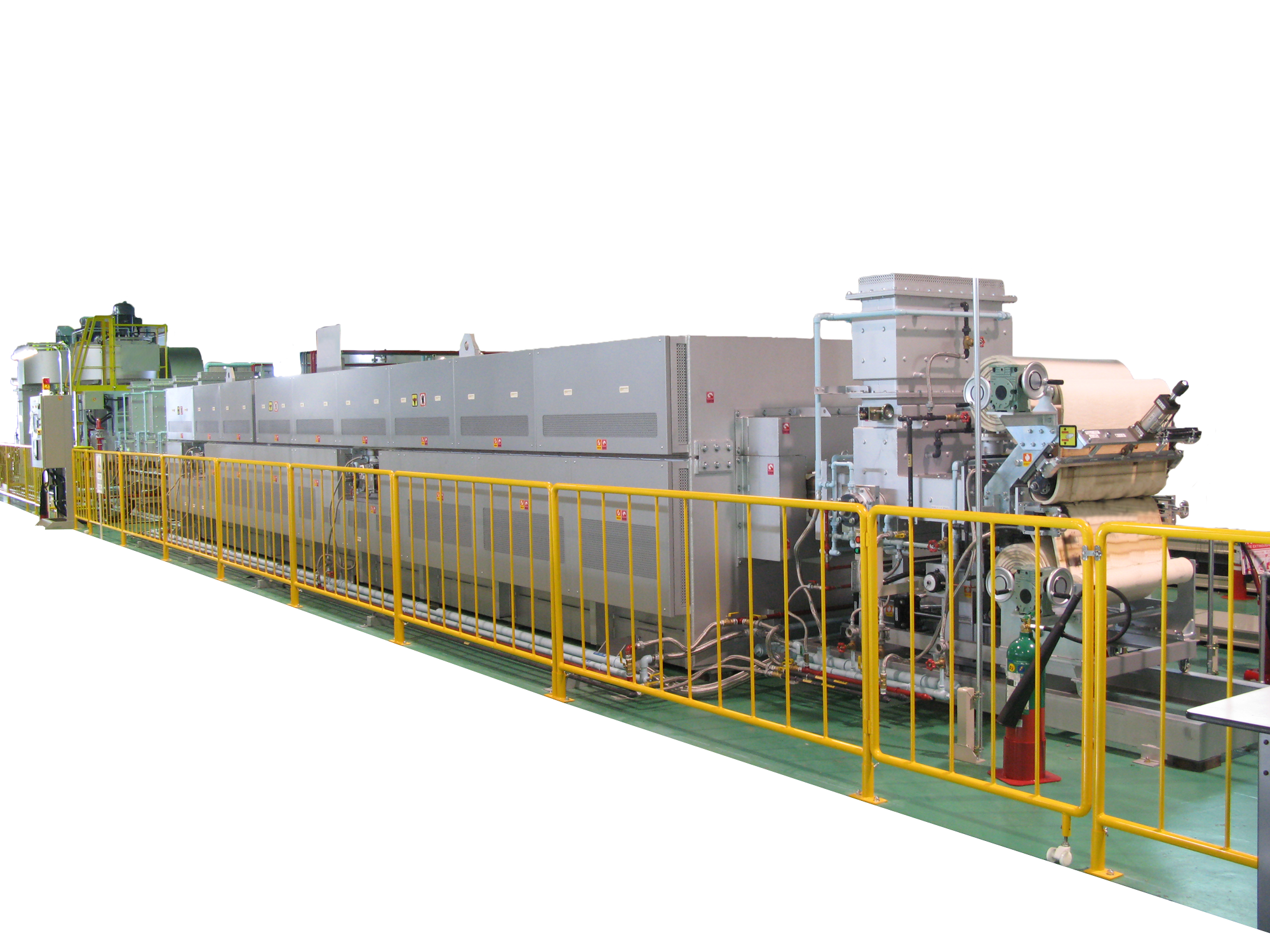
[Pre-implementation challenges]
Heat treatment of thicker plates was done, but the furnace could not handle thin plates.
[Post-implementation advantages]
By adding a lift roll in the muffle, the roll position can be adjusted according to the plate thickness. As a result, the furnace can handle both thick and thin plates, leading to cost savings.
Summary
In this article, we have explained the mechanism, applications, and types of the bright annealing process and the bright annealing furnace.
Bright annealing is a type of annealing process that is used to produce products with a glossy finish, such as stainless steel.
When annealing is performed under atmospheric conditions, an oxide film is generated, which can cause the surface to darken. In bright annealing, a gas atmosphere containing hydrogen, nitrogen, or ammonia decomposition gas is used to prevent oxidation.
The right furnace type, size, and heating conditions are chosen based on the product’s substance and size.
By designing a robust system from the outset, it becomes easier to maintain and improve, and the system’s versatility is increased.
At industrial furnace manufacturer Sun Furnace, we propose custom-made bright annealing furnaces tailored to your needs using the expertise we have gained from producing over 1,500 industrial furnaces.
We also offer free technical consultations, so please feel free to contact us.



